24 lignesA muscarinic receptor antagonist is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity …
Electrophysiological correlates of respiratory failure in
Organophosphate poisoning
Muscarinic poisoning 30 min – 2 h: Muscarine is similar to acetylcholine, but unlike acetylcholine it is not broken down by acetylcholinesterase, thus leading to overstimulation of the peripheral muscarinic cholinergic receptors e1, e2, Vomiting, …
Muscarinic toxicity among family members after consumption
Muscarine
In literature various systemic toxic syndromes associated with mushroom poisoning have been described We report four members of a family with muscarinic manifestations after accidental consumption of poisonous mushrooms The Clitocybe species of mushrooms they consumed resulted in their muscarinic toxicity, Patients with muscarinic mushroom toxicity have early onset of symptoms …
Atropine
Muscarine
Overview
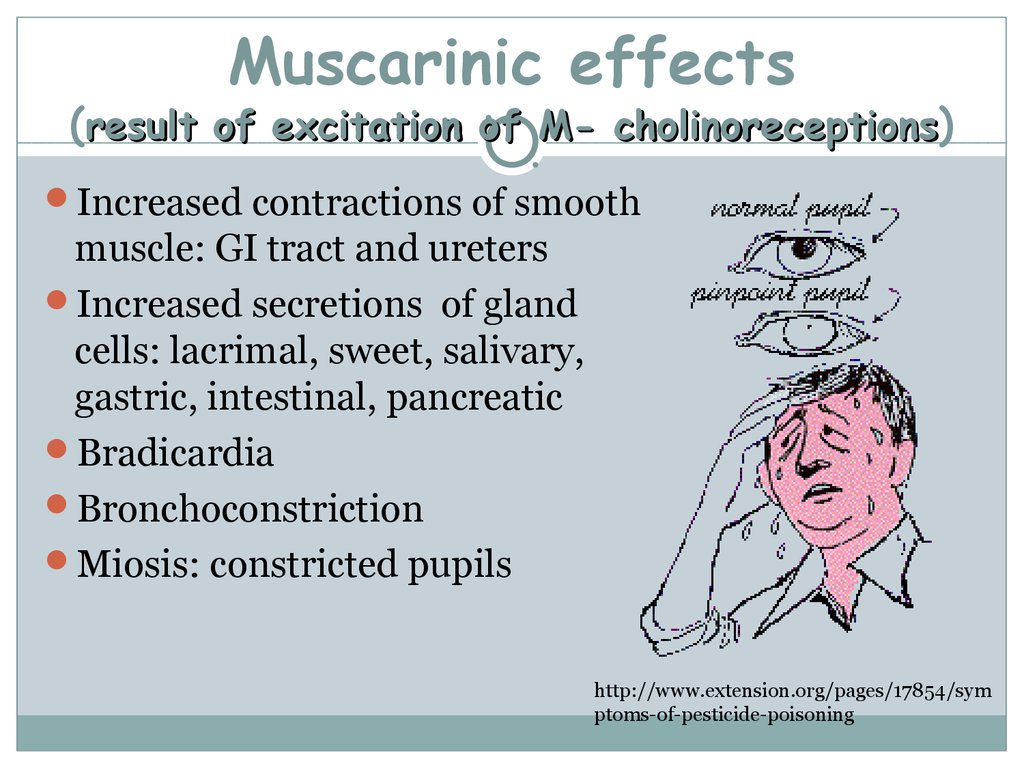
Muscarinic effects by organ system include the following: Respiratory – Rhinorrhea bronchorrhea bronchospasm cough, severe respiratory distress, Gastrointestinal – …
A mixture of signs and symptoms can occur with muscarinic poisoning from medications or mushrooms Manifestations may vary even among persons who ingested mushrooms grown in the same patch and gathered at the same time Confusion can occur if mushroom poisoning is attributed to a suspected species rather than to the toxin suggested by signs and symptoms, Accurate diagnosis …
Conclusion: The normal RNS in all patients developing early respiratory failure suggests that it is due …
Cholinergic Toxicity
Mushroom Poisoning
Atropine or atropine sulfate carries FDA indications for anti-sialagogue/anti-vagal effect, organophosphate/muscarinic poisoning, and bradycardia, Atropine acts as a competitive, reversible antagonist of muscarinic receptors: an anticholinergic drug, This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, safe administration, adverse effects, contraindications, toxicology, and …
Muscarinic Agonists
Muscarinic poisoning from medications and mushrooms A
Acetylcholine accumulation at muscarinic receptors produces an increase in secretions which can manifest as bronchorrhea, salivation, tearing and sweating, bronchoconstriction, tightness in the chest, wheezing, bradycardia, vomiting, increased gastrointestinal motility, abdominal tightness, diarrhea, and cramps, Activation of muscarinic receptors in the eye by excess acetylcholine will …
Muscarinic agonists are parasympathomimetic drugs and are indicated for ileus, urinary retention, glaucoma, Alzheimer disease, and other symptoms, This activity describes the indications, contraindications, and possible adverse effects of muscarinic agonists and how the interprofessional team can work together to improve outcomes using these agents, This activity will also highlight the …
Muscarinic toxicity presents with an unusual and unique constellation of symptoms but may also go unrecognized, The usual symptoms and signs associated with muscarinic stimulation are exhaustion, irritability, muscular cramps, salivation, frothing, sweating, lacrimation, blurring of vision, miosis, ptosis, bronchorrhea, cough, tachypnea, bronchospasm, bradycardia, hypotension, abdominal cramps, …
What are the muscarinic symptoms of organophosphate OP
Organophosphate poisoning is poisoning due to organophosphates, Organophosphates are used as insecticides, medications, and nerve agents, Symptoms include increased saliva and tear production, diarrhea, vomiting, small pupils, sweating, muscle tremors, and confusion, While onset of symptoms is often within minutes to hours, some symptoms can take weeks to appear, Symptoms can last for days …
Clinical features of organophosphate poisoning: A review
Muscarinic antagonist
Respiratory symptoms are common in OP poisoning Muscarinic effects of salivation rhinorrhea bronchorrhea and bronchospasm contributed to hypoxemia and increased work of breathing Nicotinic effects result in muscle weakness and paralysis and predispose to hypercapnic respiratory failure Central effects of agitation restlessness and seizures further compromise respiratory function,
muscarinic poisoning